SMBs and mid-market organizations are confronting an unprecedented convergence of cyber risks in 2026. The rise of AI-powered attacks means threats are more targeted, faster, and harder to detect. Ransomware groups now operate with exceptional speed, often combining data exfiltration and rapid extortion cycles. Organizations must also navigate evolving disclosure requirements and mounting scrutiny around third-party and supply chain risks—all while working with limited budgets and understaffed IT and security teams.
This guide provides a clear, actionable resource tailored for business and technology leaders who face the daunting reality of a cyber threat environment that outpaces traditional defenses. You’ll find a breakdown of what’s changed in 2026, a pragmatic assessment of which security controls deliver measurable value, and a step-by-step framework to prioritize improvements. Our 30/60/90-day action plan is designed to build resilience and protect your business without hampering agility—empowering you to balance robust security with operational efficiency.
Free Cyber Maturity Review
Get a prioritized scorecard and a practical roadmap for the next 90 days.
Book a Cyber Maturity ReviewWhy Cyber Risk Looks Different in 2026
While core attack categories—phishing, credential theft, ransomware—haven’t changed, speed and scale have. Generative AI and automated tooling let adversaries tailor social engineering at volume, probe external attack surfaces continuously, and move laterally faster once inside a network. Meanwhile, regulators and insurers demand clearer proof that basic controls are in place.
For SMB and mid-market leaders, the 2026 mandate is simple: focus on implementing the few controls that consistently block the majority of incidents, then prove effectiveness with simple metrics executives understand. That means identity-centric security, well-managed endpoints, modern detection and response, immutable backups, and a right-sized governance cadence that doesn’t stall productivity.
Trend #1: AI-Driven Attacks & the Defense Response
Attackers now leverage advanced AI to craft large-scale, highly convincing phishing campaigns that easily bypass traditional detection. AI-powered deepfake audio enables sophisticated executive impersonation, making business email compromise and CEO fraud more believable and far-reaching. Automation accelerates reconnaissance, allowing adversaries to scan for vulnerabilities such as leaked credentials on the dark web, inadequate multi-factor authentication, and unpatched edge devices at unprecedented speed. Even modestly skilled threat actors can stitch together off-the-shelf tools and AI-generated content to identify exploitable gaps in your environment and target weak links before defenses can catch up. This new wave of accessible, scalable attack methods raises the bar, requiring organizations to rethink how they detect, block, and respond to high-volume, AI-driven threats.
What good looks like
- Phishing-resistant authentication: move critical apps to FIDO2/WebAuthn or device-bound passkeys; reduce OTP fatigue prompts.
- Adaptive access: enforce conditional access policies that evaluate user, device health, location, and risk in real time.
- AI for defense: enable behavior-based detection in EDR/XDR and email security; tune models with your environment data.
- Human-in-the-loop: ensure a 24×7 triage function (internal or managed) to validate alerts and contain them quickly.
Quick wins
- Turn on impersonation protection and brand indicators (BIMI/DMARC alignment) for outbound trust.
- Disable legacy auth; enforce MFA on all external access; shorten session lifetimes for privileged roles.
- Run a targeted “CEO fraud” tabletop that includes finance approval workflows.
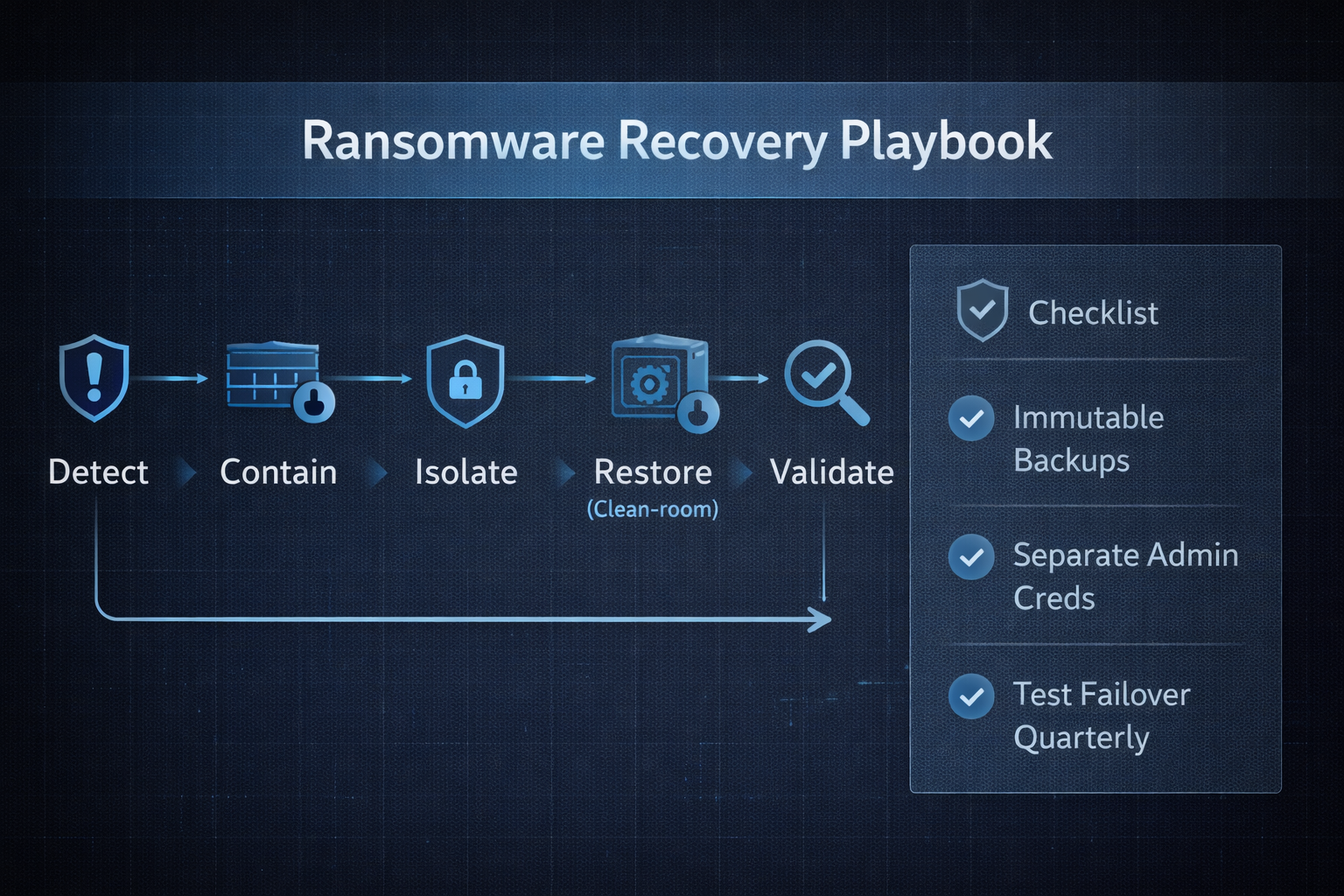
Trend #2: Ransomware’s New Playbook
Ransomware crews today have shifted tactics, prioritizing the theft of sensitive data before deploying encryption. They maximize leverage by imposing extremely short extortion deadlines, forcing organizations to make high-pressure decisions. Attackers increasingly target exposed remote access points, such as unsecured RDP or VPN services, as well as unmanaged or outdated endpoints and networks that lack segmentation. A flat network architecture enables rapid lateral movement, escalating the risk of broad compromise. Even reliable backups no longer guarantee recovery—adversaries frequently attempt to locate, corrupt, or delete backups as part of their attack sequence, aiming to eliminate restoration options and further strengthen their negotiating position.
Defensive priorities
- EDR everywhere: standardize on one vendor; ensure tamper protection and consistent policy across all endpoints.
- Network containment: segment high-value systems; use least-privileged service accounts; restrict east-west traffic.
- Backup resilience: maintain immutable, offline copies; test restore times; secure backup admin paths separately.
- Incident playbooks: pre-approve decisions (isolate, power down, engage legal/PR/forensics) to cut hours off response.
Signals that you’re improving
- Time to detect (TTD) and time to contain (TTC) measured in minutes, not days.
- Monthly restore tests meet RTO/RPO targets for critical apps and file shares.
- Phishing simulation failure rates are trending down with role-based training.
Trend #3: Practical Zero Trust—Identity, Endpoint, & Data
Zero Trust is no longer a theory—it’s a prioritization framework that governs real, everyday decisions. For SMBs, practical Zero Trust implementation starts by focusing on three pillars: identity, device health, and data access. The journey begins with strong multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all users and with the deployment of conditional access policies that evaluate user risk, device compliance, and location before granting access to sensitive resources. Next, layer in device compliance checks—ensuring only managed, up-to-date devices can access core applications—to shrink attack surface and block lateral movement from compromised endpoints. Finally, define and enforce precise data access controls by mapping roles to job functions, applying sensitivity labels to critical information, and monitoring for anomalous data usage. This phased approach empowers organizations to implement meaningful security improvements—contain breaches, reduce overexposure, and demonstrate measurable progress—all while maintaining operational agility.
30/60/90 for Zero Trust
- 30 days: inventory identities; disable dormant accounts; enforce MFA; block legacy protocols.
- 60 days: roll out conditional access baselines; require compliant devices; implement privileged access workstations.
- 90 days: apply data classification/labels; restrict external sharing; monitor for policy hits and adjust.
The aim isn’t perfection—it’s to narrow the blast radius so that single-factor credentials or a compromised laptop can’t jeopardize the business.
Trend #4: Third-Party & Supply Chain Risk Gets Real
Vendors extend your attack surface. In 2026, customers and regulators expect organizations to demonstrate not just initial due diligence, but also ongoing vigilance. This means proactively assessing vendor security practices, requiring continuous monitoring of critical integrations, and ensuring that any supplier-related incident triggers immediate, transparent communication. When a third-party event has the potential to impact your data or disrupt your operations, the expectation is rapid notification, clear updates, and documented evidence of your oversight. Ultimately, your ability to manage and communicate vendor risk is now a core component of both operational resilience and customer trust.
What to implement
- Standardized security questionnaires aligned to your control set (e.g., MFA, EDR, backups, logging).
- Tiering and scopes: classify vendors by data and privilege; apply deeper checks to high-risk integrations.
- Contractual hooks: right to audit, breach notification windows, minimum controls, and evidence of testing.
- SBOM/patch cadence: request software bill of materials for critical apps; track vulnerability remediation SLAs.
Communication matters
Draft pre-approved templates for customer notifications; rehearse with legal and PR; keep logs and tickets that evidence due diligence.
Trend #5: The Hidden Cyber Gaps in Hybrid Work
Hybrid work has made unmanaged networks, shared home devices, and data sprawl across personal tools the norm—introducing critical security blind spots for SMBs and mid-market organizations. The solution isn’t intrusive employee surveillance or blanket monitoring. Instead, today’s leaders must set clear, user-friendly guardrails and implement friction-smart controls that respect privacy while protecting business data. This means defining acceptable device and data usage in policy, offering secure remote access that doesn’t overwhelm users with complexity, and enabling adaptive controls that respond to context—such as requiring extra authentication on unmanaged devices or restricting downloads of sensitive data on personal computers. By focusing on practical boundaries and security measures that fit naturally into hybrid workflows, businesses can reduce risk without sacrificing productivity or employee trust.
Close these gaps first
- Endpoint management: enforce full-disk encryption, screen lock, and OS patching; block execution of unknown drivers.
- Secure access service edge (SASE): broker access to SaaS and private apps; inspect traffic without backhauling everything.
- DLP with context: use sensitivity labels and just-in-time prompts rather than hard blocks that stall work.
- BYOD policies: separate work profiles on mobile; restrict synchronization of classified data to unmanaged devices.
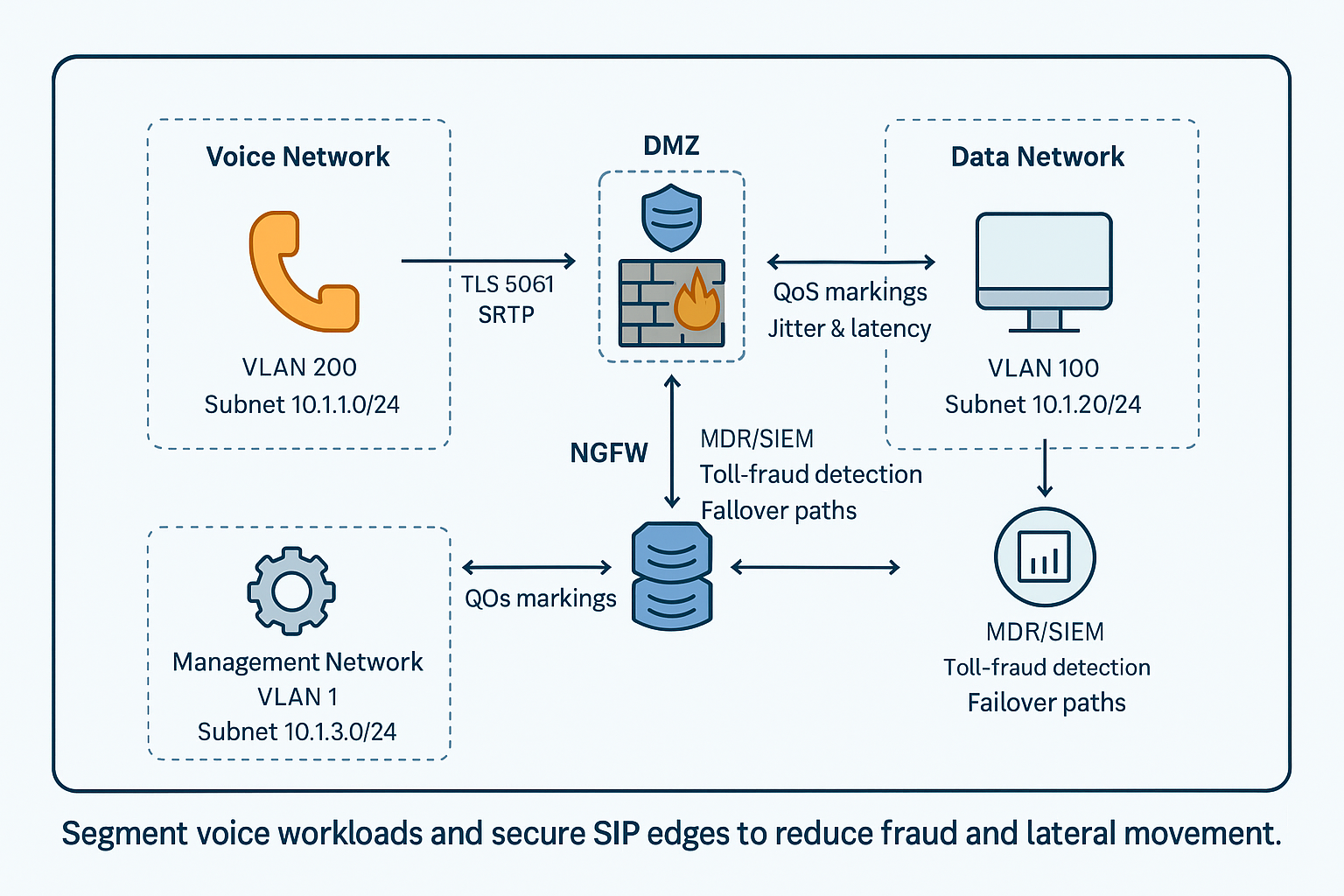
Trend #6: Voice & Data Infrastructure as a Security Surface
Telephony and collaboration stacks—SIP trunks, PBXs, UCaaS platforms, and contact centers—play a vital role in ensuring business uptime and serve as an often-overlooked attack vector for fraud and operational disruption. Threat actors target these systems by exploiting exposed SIP interfaces, leveraging weak or default administrative credentials, and exploiting flat network segments with insufficient segmentation. Successful compromise can enable attackers to pivot deeper into your environment, intercept sensitive communications, or initiate toll fraud schemes that drive up costs and evade detection through automated calling bots or international call routes. As organizations extend voice and collaboration into hybrid work and cloud environments, the attack surface expands, making continuous monitoring, network segmentation, and strong authentication critical to minimizing risk and preserving communications resiliency.
Hardening moves
- Enforce strong auth and IP allowlists for SIP trunks and admin portals.
- Segment voice networks and apply QoS alongside security controls to avoid jitter tradeoffs.
- Monitor for anomalous call patterns and geographies; set rate limits and auto-shut rules.
- Document failover paths and test them—especially for emergency services and contact centers.
Trend #7: Cyber Insurance Requirements Tighten
Insurers are raising the bar for cyber insurance eligibility and pricing. Today, it’s standard for underwriters to mandate verified proof that foundational controls are not only implemented but also continuously effective before issuing a quote or approving a renewal. Expect detailed scrutiny of universal multi-factor authentication (MFA) across all entry points, the deployment of endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions with centralized visibility, immutable backup strategies, stringent privileged access management, defined vulnerability patching service level agreements (SLAs), and documented, actionable incident response plans. Insurers may request attestation reports, technical screenshots, or evidence from your technology stack to confirm these requirements are met. The more robust and well-documented your control evidence, the faster and more smoothly the renewal process will proceed, minimizing friction and accelerating coverage decisions at a time when delay can put operational continuity and compliance at risk.
Prepare your dossier
- Control summaries mapped to frameworks (e.g., NIST CSF 2.0) with attestation dates.
- Screen captures or reports from MFA, EDR/XDR, backup immutability, and vulnerability management.
- IR plan with roles, contact trees, and vendor retainer agreements.
- Quarterly governance notes showing leadership reviews and actions.
Governance & Disclosure: What Mid-Market Leaders Should Expect
Even if you’re not a large public filer, the expectations for transparency and accountability have fundamentally shifted. Customers, partners, and regulators now routinely demand prompt and thorough disclosure of significant cyber incidents, greater clarity in how cyber risks are governed, and direct board involvement in oversight. For mid-market organizations, aligning with these expectations doesn’t require the resource burden of large enterprises. Instead, practical governance means instituting a reliable but efficient rhythm—such as setting quarterly risk reviews with executive participation, utilizing concise security dashboards for at-a-glance insight, and preparing incident notification templates in advance. This approach ensures your stakeholders receive timely, credible information, and your leadership stays engaged with evolving threats, all while minimizing operational drag. By proactively embracing this cadence, you not only strengthen trust but also demonstrate maturity in your risk management—key factors in winning business and satisfying regulatory obligations.
Right-sized governance cadence
- Quarterly risk review: top 5 risks, control status, incidents, and actions.
- Metrics that matter: coverage (% endpoints with EDR/MFA), mean time to contain, backup restore success, critical vuln age.
- Decision logs: document what you accepted, transferred, or mitigated and why.
Your 30/60/90-Day Action Plan
FIRST 30 DAYS: CLOSE THE BIGGEST DOORS
- Turn on MFA for every external entry point; remove legacy auth; set conditional access baselines.
- Deploy/standardize EDR across all Windows/macOS/Linux endpoints; enable tamper protection.
- Inventory admin accounts; enforce just-enough access; rotate shared secrets.
- Validate backup immutability; run a timed restore test for a critical workload.
Next 60 days: contain & observe
- Implement network and identity segmentation for privileged systems.
- Route logs to a centralized platform; ensure 24×7 alerting (in-house or MDR).
- Roll out data classification and basic DLP policies tied to labels and locations.
- Tabletop: ransomware with data exfiltration; include legal, finance, and PR.
By 90 days: prove it & scale
- Publish a one-page executive dashboard with the metrics below.
- Automate patch SLAs and exception handling; review top 10 risky controls monthly.
- Finalize vendor tiering; require minimum controls and notification terms in contracts.
Metrics That Prove Progress
- Coverage metrics: % users with MFA enforced; % endpoints with healthy EDR; % data with sensitivity labels.
- Time-based metrics: mean time to detect/contain; patch time for critical vulns; restore time for priority apps.
- Outcome metrics: phishing failure rate; blocked lateral movement attempts; successful restore rate.
- Vendor risk metrics: % high-risk vendors with minimum controls; average remediation SLA adherence.
Ready to turn this into a 90-day plan?
Get a prioritized scorecard, architecture recommendations, and a quick-win rollout sequence.
Book a Cyber Maturity ReviewFAQs
WHAT ARE THE MOST IMPACTFUL CONTROLS FOR SMBS IN 2026?
Enforce phishing-resistant MFA, deploy a single EDR platform across every endpoint, centralize logging with 24×7 monitoring, maintain immutable backups, and apply least-privilege access for admins. These reduce the majority of real-world incidents.
How do we start Zero Trust without disrupting productivity?
Begin with identity and device health: require MFA and compliant devices for key apps, then phase in data classification and conditional access. Pilot with a small group, measure impact, and expand in rings.
What does a solid ransomware posture look like?
EDR everywhere, segmented networks, immutable/offline backups with tested restores, and a rehearsed incident playbook. Add email and web threat protection and tighten privileged access workflows.
How should we handle third-party risk without boiling the ocean?
Tier vendors by data sensitivity and system access, require a minimum control set for high-risk integrations, and monitor remediation SLAs. Use contracts to set notification windows and audit rights.
What metrics convince executives & insurers we’re improving?
Coverage (% MFA, % EDR), time-based (MTTD/TTC, patch time), outcome (restore success, phishing failure rate), and vendor controls coverage.
Cyber Advisors delivers end-to-end expertise across advisory services, engineering, and 24×7 managed security operations—enabling SMB and mid-market organizations to defend against today’s advanced threats while staying agile. Our national reach ensures clients receive consistent, enterprise-grade security and IT guidance wherever they operate, with select services delivered locally in Chicagoland through our trusted subsidiaries, Chicago Voice & Data and DigiTek Security. As a Cyber Advisors company, these teams extend our capabilities, helping you modernize critical IT and communications infrastructure, harden your security posture, and achieve compliance—backed by responsive support and deep technical know-how.